There are real technology implications to these new Internet applications.
First is the need for increased bandwidth. Internets, intranets, and extranets have totally reversed the 80/20 rule so that now 80% of the traffic is going over the backbone and only 20% is local. Everyone is clamoring for Fast Ethernet and even Gigabit Ethernet connections.
The need for security is obvious once a company is connected to the Internet. You cannot read the paper without hearing about the latest hacking job.
The Internet makes VPNs possible.
And finally, EDI to enable electronic commerce.
We’ll look at each of these briefly.
Applications Need Bandwidth
The type of connection necessary depends on the bandwidth required:
– Individual users connecting to the Internet for e-mail or casual Web browsing can usually get by using a simple modem.
– Power users or small offices should consider ISDN or Frame Relay.
– Larger offices or businesses that expect high levels of Internet traffic should look into Frame Relay or leased lines.
– New technologies like asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) and high-data-rate digital subscriber line (HDSL) will make high-speed Internet access even more affordable in the future.
Internet Security Solutions
One of the most vulnerable point in a customer’s network is its connection to the Internet. To secure the communication between a corporate headquarters and the Internet, a customer needs all the integrity security tools at its disposal. These tools include firewalls, Network Address Translation (NAT), and encryption, token cards, and others.
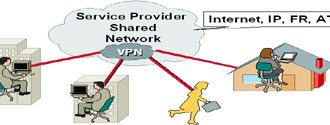
Virtual Private Network
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) can bring the power of the Internet to the local enterprise network. Here is where the distinction between Internet and intranet starts to blur. By building a VPN, an enterprise can use the “public” Internet as its own “private” WAN.
Because it is generally much less expensive to connect to the Internet than it is to lease data circuits, a VPN may allow companies to connect remote offices or employees when they could not ordinarily justify the cost of a regular WAN connection.
Some of the technologies that make VPNs possible are:
- – Tunneling
- – Encryption
- – Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Electronic commerce can streamline regular business activities in new ways. Have any of you used a fax machine to send purchase orders to vendors?
A fax machine turns your PO into bits, transmits them across a network, and then turns them back into atoms on the other end. The disadvantage is that the atoms on the other end can only be read by a human being, who probably has to retype the data into another computer.
EDI provides a way for many companies to reduce their operating costs by eliminating the atoms and keeping the bits.
What advantages does EDI provide your customer?
- – Ensures accurate data transmission
- – Provides fast customer response
- – Enables automatic data transfer—no need to re-key
For example, RJR Nabisco reduced PO processing costs from $70 to 93 cents by replacing its paper-based system with EDI.
Public key/private key encryption is created by the PGP program (Pretty Good Privacy). It creates a public key and a private key. Anyone can encrypt a file with your public key, but only you can decrypt the file. To ensure security, an enterprise may issue a public key to its customers, but only the enterprise will be able to decrypt a message using the private key.
– SUMMARY –
The Internet has created the capability for almost ANY computer system to communicate with any other. With Internet business solutions, companies can redefine how they share relevant information with the key constituents in their business—not just their internal functional groups, but also customers, partners, and suppliers.
This “ubiquitous connectivity” created by Internet business solutions creates tighter relationships across the company’s “extended enterprise,” and can be as much of a competitive advantage for the company as its core products and services. For example, by allowing customers and employees access to self-service tools, businesses can cost effectively scale their customer support operations without having to add huge numbers of support personnel. Collaborating with suppliers on new product design can improve a company’s competitive agility, accelerate time-to-market for its products, and lower development costs. And perhaps most importantly, integrating customers so that they have access to on-time, relevant information can increase their levels of satisfaction significantly. Recapping:
– Internet access can take a business into new markets, decrease costs, and increase revenue through e-commerce applications. It can attract retail customers by providing them with company information and the ability to order online.
– Intranets can provide your employees with access to information and help compress business cycles.
– Extranets enable effective management of your supply chain and transform relationships with key partners, suppliers, and customers.
– Voice/data integration can save companies significant amounts of money and, at the same time, enable new applications.
– All of these applications reduce costs and increase revenue.